 |
 |
 |
Fungal Diseases
Powdery Mildews (Erysiphaceae)Powdery mildew of Cucurbits Powdery mildew of Strawberry Powdery mildew of Marple Powdery mildew of Roses Powdery mildew of Grape Powdery mildew of Oak Powdery mildew of Goosberry and Black Currant Powdery Mildew in general.......Diseases caused by different kind of powdery mildews, are very common on our cultivated Plants, both in- and outside our houses. Perhaps you could say, also on many "wild" growing Plants.The chalk-white, dusty spots, most often on the upper leaflets, after some time they are floating together, are the normal symptoms from a powdery mildew attack. Powdery mildews are to be spread to stalks and stems (sometimes fruits) and they can be found also over wintering in branches and buds. 
Typical white, covering on cucumber leaves
are the certain symptom of powdery mildew (Erysiphe cichoracearum).
Photo: Magnus Gammelgaard Powdery Mildews belong to the group of fungi called Erysiphaceae. They are all obligatory parasitic (they can not live, reproduce and survive without the host plant), otherwise it is, with for instance Grey Mould, which can grow on different, artificial medias. Typical for Powdery Mildews are also that they are very host specific. For instance will Powdery Mildew of roses not be able to grow on apples and reverse. Often this dividing into groups of genus is very common. Powdery mildew on apple will be able to infest species within the genus of malus. 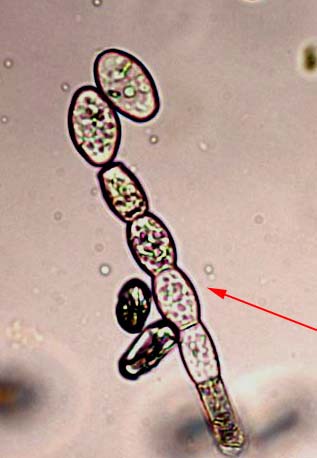
Microscope photo of conidia formed in long
chains.
The conidia breaks and are blown away by the wind. Here Powdery mildew of cucurbits (Erysiphe cichoracearum). Photo: Magnus Gammelgaard Hot and dry weather favourite the forming of the conidia and the spreading by the wind, while the germination are favourite by high humidity, though there should not be resisting water on the leafs. When conidia have landed on the surface of a leaf it first develop a so-called appendage. After that a germ tube will penetrate the cell wall and a haustoria (organ to pick up nutrients) will be formed inside the plant cell. After some time new conidia are formed and blown away by the wind to new plants. Heavily attack from Powdery Mildews are often totally destroying vegetables, whereas ornamentals rarely are dying. Countermeasures:
|
|
Control
Normally it cannot be recommended to use chemical fungicides in private gardens. But the following chemicals have an effect on powdery mildews.
"Family remedy":Spraying with skimmed milk has some effects on powdery mildews. It cannot be recommended for use inside our houses because the smell of sour milk is too penetrating. Natriumbenzoat (Atamon) normally uses for making jam or other preservative purposes. This has an effect on powdery mildew. The recommended dose is 40 ml of Atamon in 1 litter of water. There is a risk of damaging the leaves if you are spraying in bright sunshine or having sensible plants. Attention should here be made. This chemical is not approved to be used as a plant protection compound. (only when making jam). Silicon: Documented investigations show that the contents of silicon in plants have an importance for avoiding heavy attack from mildews. Or you could say that silicon strengths the immune defence system. In the moment trials are being carried out with adding silicon to soluble plant fertilizer to cucurbits. Extract from the Horsetail plant has a high contents of silicon and properly therefore it is recommended for use for plant protection. Take a look at: altrecept1.htm og altplantesygdomme.htm. Fungicides, which contain propiconazol, are used in agriculture to control powdery mildew and are very effective. Opdateret d. 26.07.2022 |
.
